Human Cardiac Fibroblasts: HCF
Description
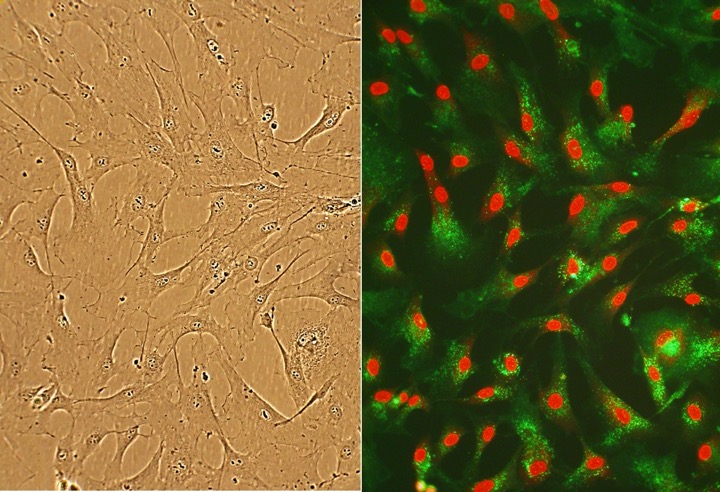
Human Cardiac Fibroblasts (HCF) are the most prevalent cell type in the heart. HCF from Cell Applications, Inc. provide an excellent model system to study many aspects of human heart function and pathophysiology.
HCF from Cell Applications, Inc. have been utilized in a numerous published studies, for example to:
- Determine that electrical coupling between cardiomyocytes and fibroblasts is mediated by Ca2+-activated K+ channels that can be stimulated by estrogen receptor agonists
- Show that antimitogenic effects of estradiol on HCF growth are mediated by cytochromes and metabolites
- Demonstrate that in response to mechanical stretch, cardiac fibroblasts release TGF-β that downregulates trombomodulin, increases thromboembolism and induces cardiac fibroblast differentiation into myofibroblasts
- Indicate that activation of G protein-coupled receptor kinase-2 prevents normal regulation of collagen synthesis in cardiac fibroblasts mimicking heart failure phenotype
- Identify FGF2 signaling pathway as potential target for modulating apoptosis in cardiac pathology
- Investigate the roles of scleraxis and AMPKα1 in scar formation following myocardial infarction
- Show that the KATP channel opener KMUP-3 preserved cardiac function after myocardial infarction by enhancing the expression of NO synthase and restoring MMP-9/TIMP-1 balance
Details
| Tissue | Normal healthy human heart tissue | |
|---|---|---|
| QC | No bacteria, yeast, fungi, mycoplasma, virus | |
| Bioassay | Attach, spread, proliferate in Growth Med | |
| Cryovial | 500,000 HCF (1st passage) frozen in Basal Medium w/ 10% FBS, 10% DMSO | |
| Kit | Cryovial frozen HCF (306A-05a, adult atrium; 306V-05a, adult ventricle; or 306-05f fetal) , Growth Medium (316-500), Subcltr Rgnt Kit (090K) | |
| Proliferating | Shipped in Gr Med, 2nd psg (flasks or plates) | |
| Doublings | At least 8 | |
| Applications | Laboratory research use only (RUO). Not for human, clinical, diagnostic or veterinary use. |
Resources
FAQs
Need More Help?
Visit our comprehensive FAQ page for detailed answers to common questions.
Need More Help?
Visit our comprehensive FAQ page for detailed answers to common questions.
Primary Cell FAQs